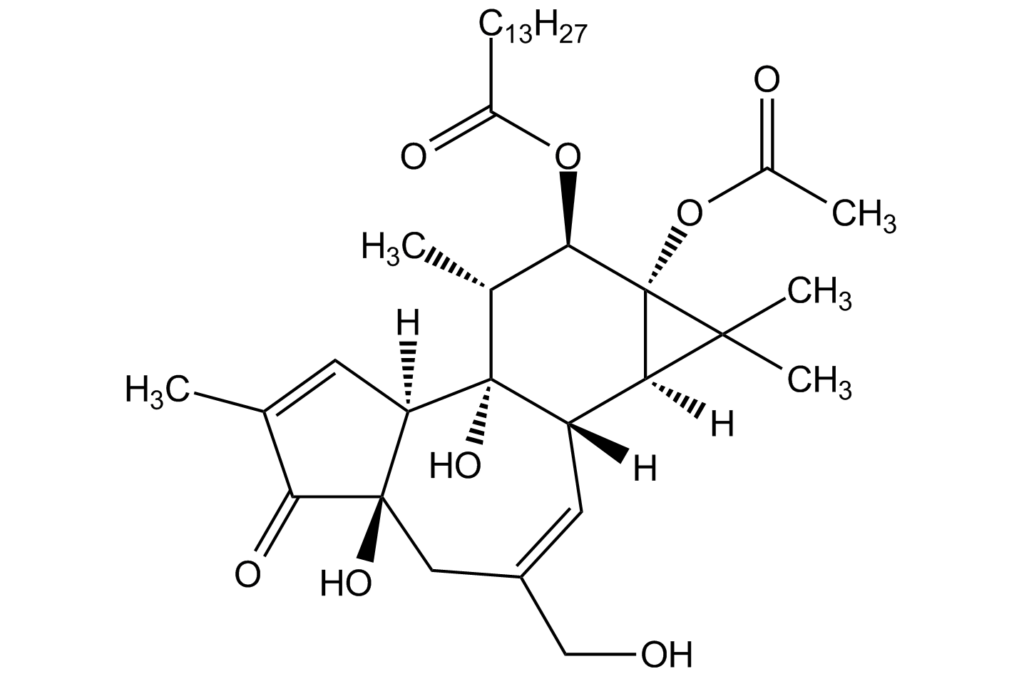
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), also known as 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate or TPA, is a naturally occurring phorbol ester found in plants like croton oil.
PMA is commonly used to activate protein kinase C (PKC), a family of enzymes involved in various cellular processes such as cell growth, differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis (programmed cell death). PMA can activate all isoforms of PKC, but it has a particularly strong affinity for PKCα, PKCε and PKCδ. PMA-activated PKC can phosphorylate a variety of target proteins, including transcription factors, signalling molecules and cytoskeletal proteins. PKC is a critical component of many signalling pathways and its activation can lead to a cascade of intracellular events.
- Cell growth and differentiation: PMA can promote cell growth and differentiation by activating PKC. This effect is thought to be mediated by the activation of genes that promote cell growth and differentiation.
- Apoptosis: PMA can also induce apoptosis or programmed cell death. This effect is thought to be mediated by the activation of genes that promote apoptosis.
- Cancer: PMA is a known tumour promoter. This means that it can increase the risk of cancer by promoting cell growth and differentiation.
- Inflammation: PMA can induce inflammation. This effect is thought to be mediated by the activation of genes that promote inflammation.
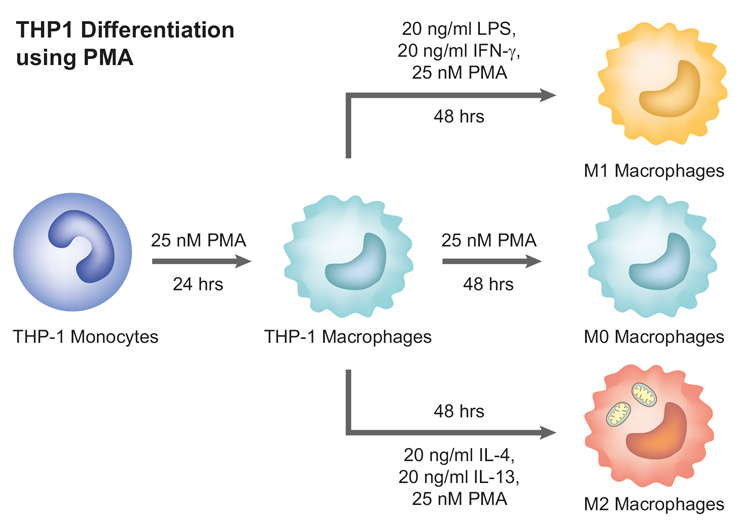
Differentiation of THP-1 Cells
The human monocytic cell line, THP-1, is the most widely used cell line for in vitro studies investigating primary human macrophage function. The reason is that following the differentiation of THP-1 cells using PMA, they acquire a macrophage-like phenotype, which mimics in many respects, primary human macrophages (M0 macrophages). PMA is a potent activator of protein kinase C (PKC), which is a key regulator of macrophage differentiation. When PMA is added to THP-1 cells, it causes them to express the surface markers CD14, CD16 and CD68, which are characteristic of M0 macrophages. PMA also induces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by M0 macrophages. Further treatment with PMA can activate M0 macrophages and differentiate them into M1 or M2 macrophages.
Activation of M0 Macrophages
M0 macrophages are a type of macrophages that are not yet fully activated. They are characterised by their expression of a variety of surface markers, including CD14, CD16 and CD68. M0 macrophages are also able to produce a variety of cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α.
The addition of PMA M0 macrophages activates them through PKC activation. Consequently, activated M0 macrophages undergo a number of changes, including the increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, increased production of reactive oxygen species, increased phagocytic activity and increased migration.
- PMA can induce the differentiation of M0 macrophages into M1 macrophages, which are pro-inflammatory cells that play a role in fighting infection.
- PMA can also induce the differentiation of M0 macrophages into M2 macrophages, which are anti-inflammatory cells that play a role in tissue repair.
- PMA can increase the production of reactive oxygen species by M0 macrophages, which can help to kill bacteria and other pathogens.
- PMA can increase the phagocytic activity of M0 macrophages, which allows them to engulf and destroy foreign particles.
- PMA can increase the migration of M0 macrophages, which allows them to travel to the site of infection or injury.
The differentiation of THP-1 cells into M0 macrophages is a complex process, important for the immune response to infection and injury.
Literature References:
- In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 1: P.M. Blumberg; Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 8, 153 (1980)
- In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 2: P.M. Blumberg; Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 8, 199 (1981)
- The choice of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate differentiation protocol influences the response of THP-1 macrophages to a pro-inflammatory stimulus: M.E. Lund, et al.; J. Immunol. Methods 430, 64 (2016)
- Standardized protocols for differentiation of THP-1 cells to macrophages with distinct M(IFNγ+LPS), M(IL-4) and M(IL-10) phenotypes: E.W. Baxter, et al.; J. Immunol. Methods 478, 112721 (2020)
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)
Other names: TPA; 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate
PMA is the most common phorbol. It is a potent tumour promoter and highly inflammatory in nature. It is a potent activator of protein kinase C (PKC), a family of enzymes that play a role in many cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. It is a standard reagent for THP1 cell differentiation.
AG-CN2-0010 (1 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 25 mg, BULK)
AdipoGen Life Sciences is an original Manufacturer of high-purity PMA. BULK quantities are available from Stock!
Product Specifications:
CAS: 16561-29-8
Source: Semisynthetic
Purity: >98% HPLC
Identity: Determined by 1H-NMR
Small Molecule PKC Agonists/Inducers/Activators
| Product Name | Product Code | Product Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ingenol-3-angelate (I3A) | AG-CN2-0012 | Specific PKC activator. |
| Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) | AG-CN2-0010 | Potent PKC activator. |
PKC Antagonist/Inhibitor/Blocker
| Product Name | Product Code | Product Description |
|---|---|---|
| Staurosporine | AG-CN2-0022 | Potent, cell-permeable, reversible, ATP-competitive broad spectrum PKC antagonist. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide I | AG-CR1-0009 | Cell-permeable, selective PKC inhibitor (Ki = 10 nM). |
| Bisindolylmaleimide I . hydrochloride | AG-CR1-0110 | Cell-permeable, selective PKC inhibitor (Ki = 10 nM), water-soluble. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide II | AG-CR1-0010 | PKC antagonist. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide III | AG-CR1-0112 | Potent and selective PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide IV | AG-CR1-0152 | Cell-permeable PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide VIII . acetate | AG-CR1-0114 | Selective PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide IX . methanesulfonate | AG-CR1-0111 | Selective, cell-permeable PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide X . hydrochloride | AG-CR1-0113 | Selective PKC inhibitor. |
| Bisindolylmaleimide XI . hydrochloride | AG-CR1-0109 | Selective cell-permeable PKC inhibitor. |
| Calphostin C | AG-CN2-0430 | Potent, highly specific, cell-permeable, light-dependent PKC antagonist. |
Negative Controls for PKC Modulators
| Product Name | Product Code | Product Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bisindolylmaleimide V | AG-CR1-0023 | Negative control for PKC inhibitors. |
| 4α-Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate | AG-CN2-0082 | Negative control for phorbol ester activation of PKC and studies with PMA. |
Originally posted by Adipogen on: https://adipogen.com/phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-pma
Caltag Medsystems is the distributor of Adipogen products in the UK and Ireland. If you have any questions about these products, please contact us.
